
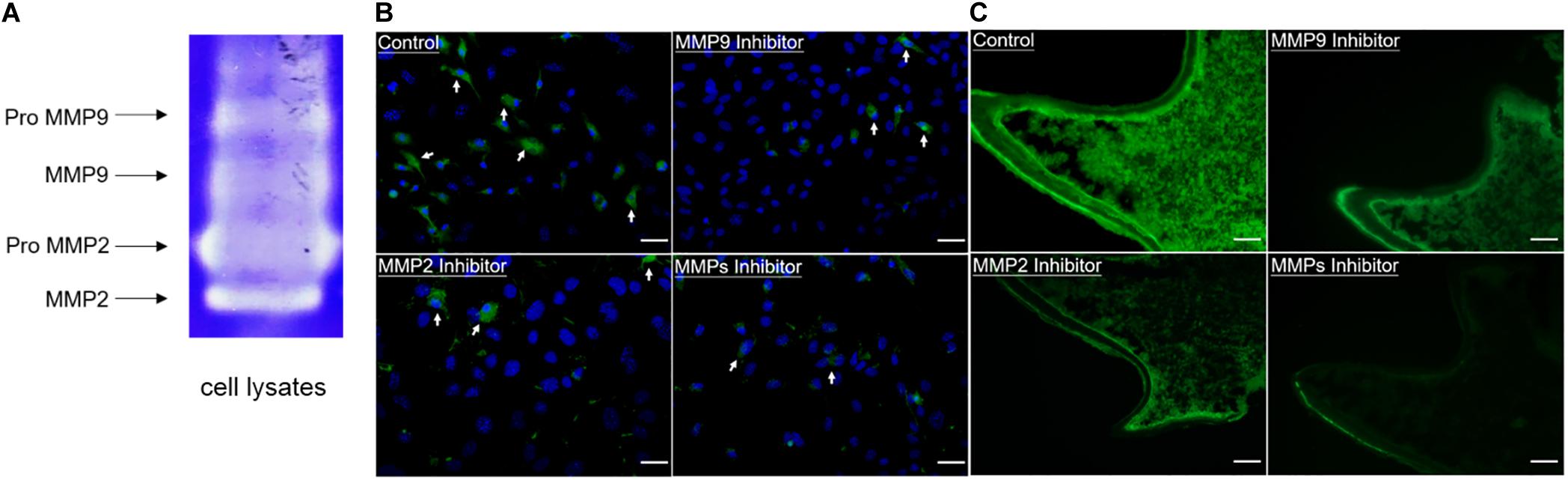
These bacteria typically reside in the gut/intestines of mammals. Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) agar is a medium used for differentiating enteric bacteria. Each pH indicator has a range of pH values over which it changes color (see below). Some common pH indicators are phenol red, bromocresol purple, and bromothymol blue. To measure this pH change, pH indicators (chemicals that change color depending on pH) are included in the medium. In many metabolic tests, end products are produced that change the pH of the medium. Image by Janie Sigmon, York Technical College, Rock Hill, SC. Image 1: Fermentation Reactions Produced by Escherichia coli in Phenol Red Sugar Broths Containing Dextrose, Sucrose, and Lactose sugars. Carbohydrate fermentation media are often used to differentiate members of the family Enterobacteriaceae (e.g., Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes) from each other. If you see a bubble in the Durham tube, the medium will also be acidic. If gases (typically CO 2) are produced during the fermentation process, a bubble will form at the top of the Durham tube (see tube A). This is a small inverted glass tube that is placed within the larger glass tube containing the fermentation medium (see image 1). To detect these gases, a Durham tube is used. Some bacteria will produce gases when fermenting a carbohydrate. In this case, the medium will become more alkaline and appear red (see image 1 tube B). If the carbohydrate in the medium is fermented and acidic end products are formed, a color change to yellow will result (see image 1 tubes A and C). Occasionally, bacteria will not ferment the carbohydrate, but instead will break down proteins producing ammonia (NH 3) in the growth medium. These types of carbohydrate fermentation tubes are therefore called Phenol red (sugar) broths. The pH of the medium is adjusted to approximately 7.5, so it appears orange/red when using phenol red pH indicator.

The medium used to test carbohydrate fermentation is a nutrient broth that contains a fermentable carbohydrate (usually a monosaccharide or a disaccharide), peptone (amino acids) as well as a pH indicator. Therefore bacteria can be differentiated both based on their ability to ferment various carbohydrates, as well as the end products that result from the fermentation process. Figure 1: Carbohydrate fermentationĪlthough the ultimate substrate molecule for fermentation is always glucose, some bacteria use additional chemical reactions to convert other monosaccharides as well as disaccharides into glucose. Microbes such as yeast and bacteria are genetically engineered to produce valuable fermentation products. We use many fermentation products-as diverse as antibiotics, alcohols, and a variety of foods. There can be numerous end products from fermentation, many of which is useful for us, but not necessarily the microbes. By contrast, the waste left over after ATP production by aerobic respiration are limited to CO 2 and H 2O.
Fermentation also tends to produce waste products that can accumulate in the extracellular environment. Note that fermentation is mainly a mechanism for regenerating NAD+ when respiratory process do not occur. For example, one fermentation waste product is ethanol, its got so much stored energy it can be used in gasoline solutions to be combusted/burned to release that energy stored in its chemical bonds. Much of the original energy in the substrate remains tin the chemical bonds of organic end products, like lactic acid or ethanol. Keep in mind, microbes are very versatile, the fermentation substrate does not have to be sugars, it can include even unusual compounds like aromatics (benzoate), glycerol (sugar-alcohol), and acetylene (hydrocarbons)! The end products are characteristic of individual bacterial species. Fermentation includes the reactions of glycolysis (where a single molecule of glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate), as well as additional reactions that produce a variety of end products (acids, alcohols, gases). \)įermentation is a metabolic process that some microorganisms use to break down substrates such as glucose and other sugars when O 2 is not available or could not be used by the microorganism.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
